SHA256: 21243cb4bc953b0773d68a8eb43efd9ba80d7ff2ea293c79e0e7f64e25946059
VirusTotal link: https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/21243cb4bc953b0773d68a8eb43efd9ba80d7ff2ea293c79e0e7f64e25946059/detection
Hybrid analysis: https://www.hybrid-analysis.com/sample/21243cb4bc953b0773d68a8eb43efd9ba80d7ff2ea293c79e0e7f64e25946059/5f09e9cb351595220702dd4e
Summary
Makop ransomware encrypts user’s files and expects a ransom for the decryption key. It uses an AES256 key to decrypt important strings at runtime including a RSA public key. The process creates a mutex to ensure that it avoids infecting the system more than once and uses an entry under the Run key to establish persistence on the host. The malicious file spawns a copy of itself with a parameter which is used to attack network resources (if any). It deletes important services, the shadow copies and kills a list of processes in order to ensure that the targeted files are not locked by other applications. The malware creates two AES256 keys which will be used to encrypt the files content and the files name. For each file, another initialization vector (IV) is generated and stored in the encrypted file. The AES key used to encrypt a file is encrypted with the public RSA key and stored at the end of each encrypted file therefore the decryption is not possible without the private RSA key which is unknown at this time.
Technical analysis
Firstly the malicious process checks to see if it starts with a parameter or not, as shown in the screenshot below (as usual first parameter is the name of the file):
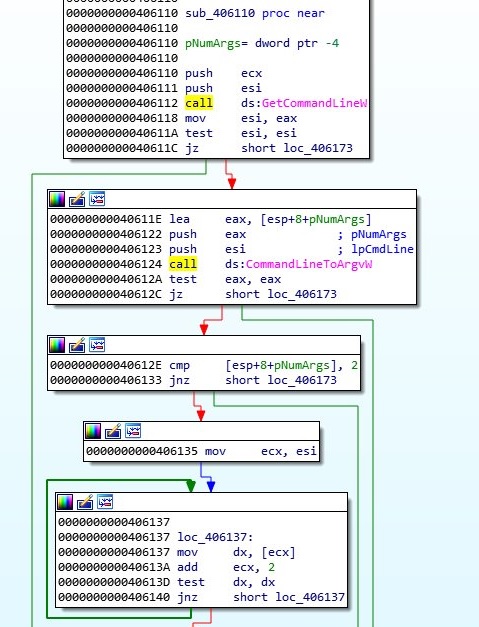
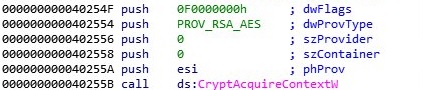
CryptAcquireContextW Windows API is used to obtain a handle to a particular key container (PROV_RSA_AES provider type):
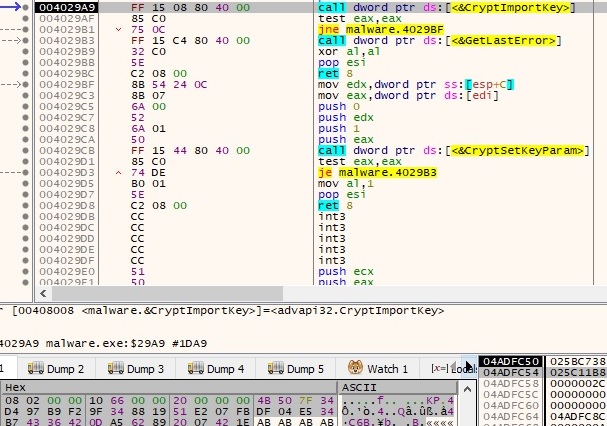
The malicious process builds a key byte by byte and this one will be used to decrypt a lot of content. It imports the key using CryptImportKey API:
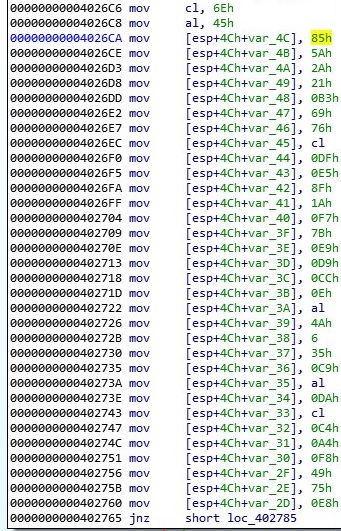
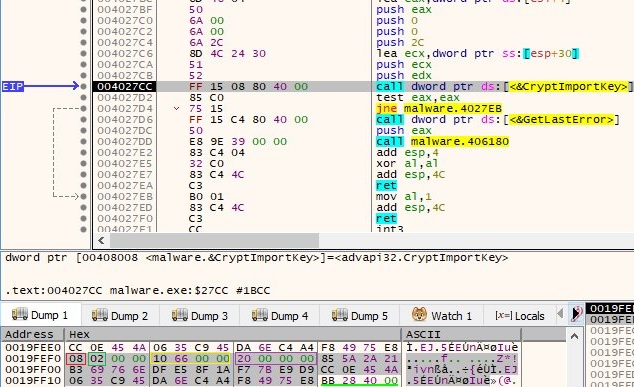
The parameters of the blob are explained as follows:
- 08 – PLAINTEXTKEYBLOB – key is a session key
- 02 – CUR_BLOB_VERSION
- 0x00006610 – AlgID: CALG_AES_256
- 0x00000020 – key length (32 in decimal)
Using the previously imported key it decrypts information which will be utilized during the entire execution:
The blob parameters are defined as follows:
- 06 – PUBLICKEYBLOB
- 02 – CUR_BLOB_VERSION
- 0x0000a400 – AlgID: CALG_RSA_KEYX
- 0x00000400 – key length (1024 in decimal)
- 0x00010001 – public exponent (65537 in decimal)
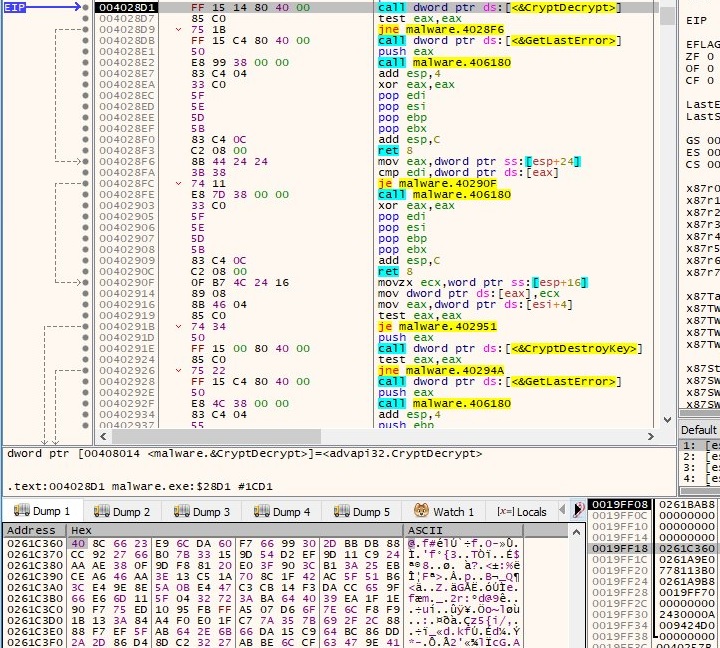
The malicious process performs a few CryptDecrypt operations in order to decrypt a few strings:
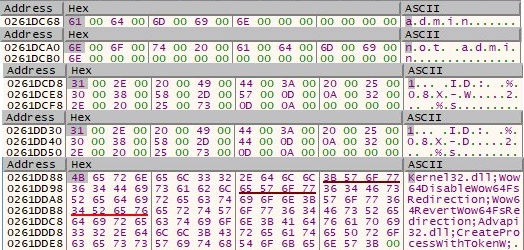
GetModuleHandleA API returns a handle to Kernel32.dll and Advapi32.dll and also the process determines the addresses of Wow64DisableWow64FsRedirection, Wow64RevertWow64FsRedirection and CreateProcessWithTokenW using GetProcAddress API. More decryption operations are performed and a few more strings are decrypted:
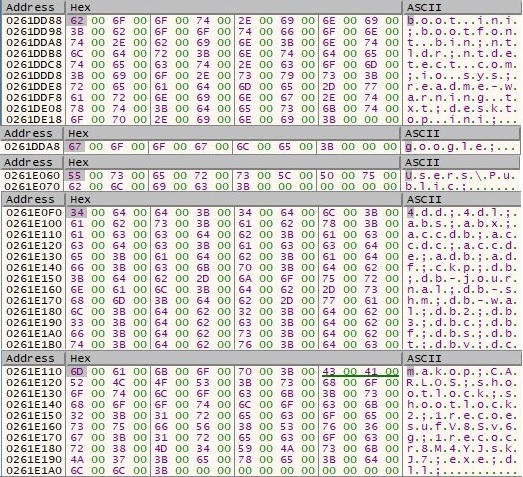
The malicious file creates a mutex called m23071644 in order to ensure that it doesn’t infect the system multiple times:
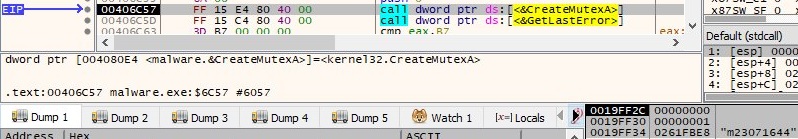
The persistence mechanism represents the creation of an entry called “1” under the registry “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run” as shown below:
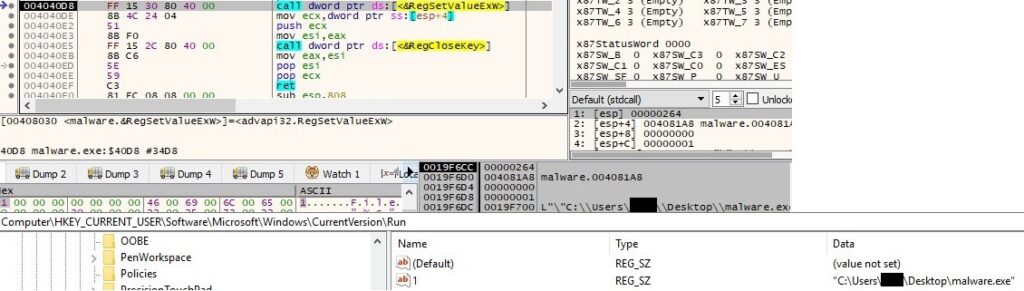
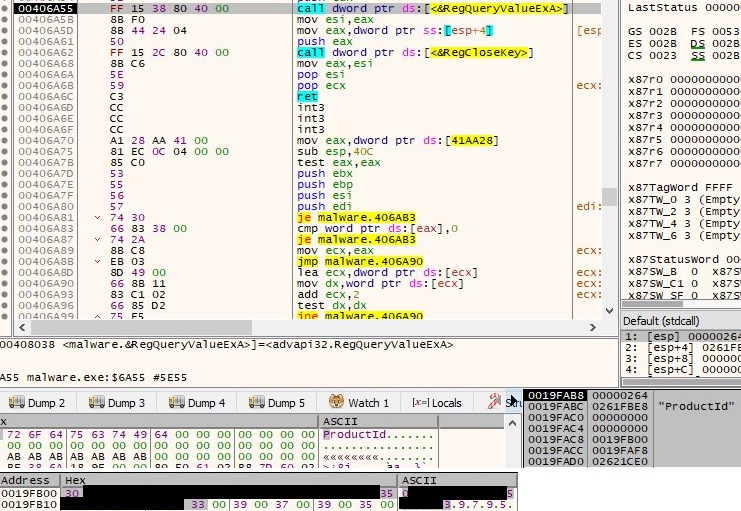
The strings “SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion” and “ProductId” are decrypted by the malware using CryptDecrypt API as before. The scope of the attacker is to obtain the Windows Product Id by querying the registry “SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProductId”:
GetVolumeInformationW API is used to collect information about the C drive such as the volume serial number. The result is concatenated with the previously product Id:
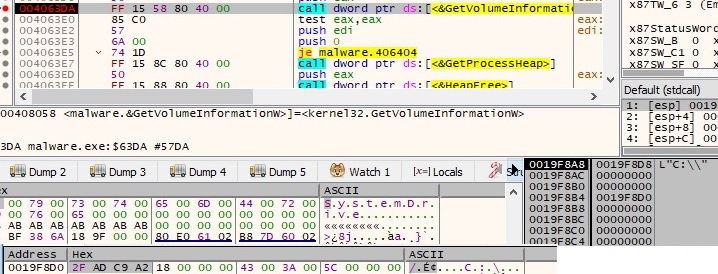
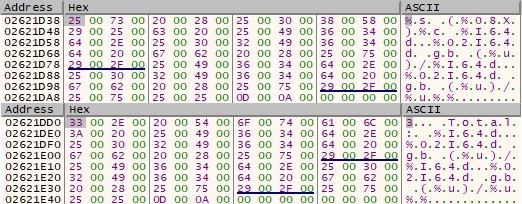
Other strings are decrypted using the imported AES256 key:
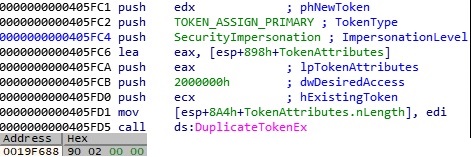
The execution continues with calling Wow64DisableWow64FsRedirection function in order to disable file system redirection for the current thread. This means a 32-bit application which is running under WOW64 is able to open the 64-bit version of another application (instead of being redirected to the 32-bit version). Later Wow64RevertWow64FsRedirection will be called to restore the file system redirection for the thread. OpenProcessToken function is used to open the access token for the current process and DuplicateTokenEx creates a new access token (primary token) that duplicates the first token:
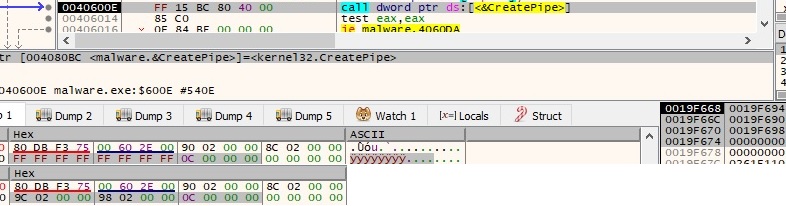
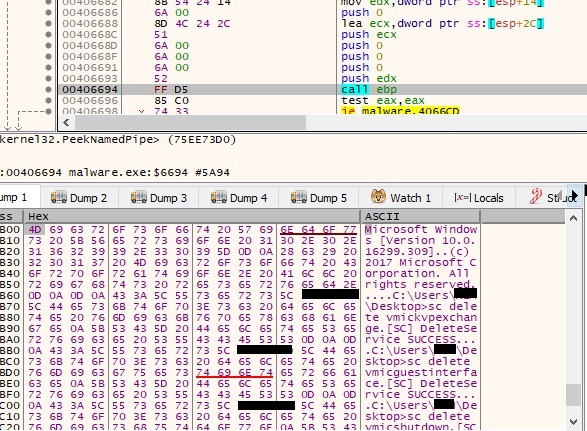
The malicious process creates an anonymous pipe using CreatePipe API and returns 2 handles (read and write handles) as shown in figure below:
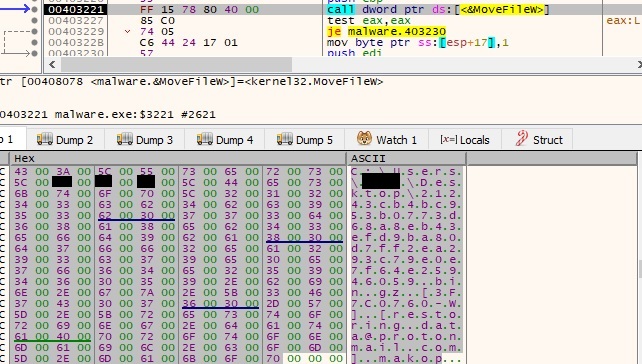
Another process is spawned by calling CreateProcessWithTokenW that executes the initial malicious file with the parameter n”Process Id of the first process” (for example n920). As we can see in the image below the first parameter is the handle of the duplicate token (0x290):
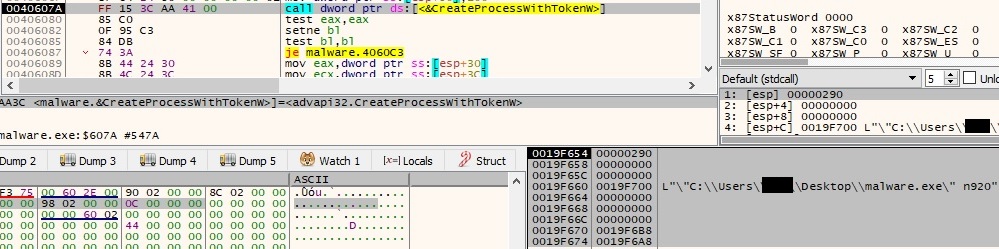
An interesting fact is the verification that the malware is indeed running with the parameter n followed by digits (process Id):
We have observed that the new process performs an enumeration of network resources or existing connections using WNetOpenEnumW and WNetEnumResourceW functions (it seems to target network shares and it is not responsible for the main encryption routine), so we will continue to analyze the initial process. GetLogicalDrives function is used to get the currently available disk drives and GetDriveTypeW returns a code which indicates if the disk is removable, fixed, CD-ROM, RAM disk or network drive (for example it returns 0x3 – DRIVE_FIXED if the drive is C ). The malware is not interested in CD-ROM drives and RAM disks:
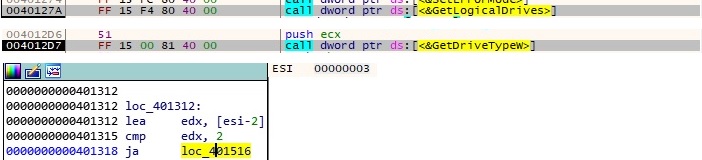
CreateFileW API is used to access the “C:” volume and then DeviceIoControl is used to obtain the physical location and disk number of “C:” as shown below:
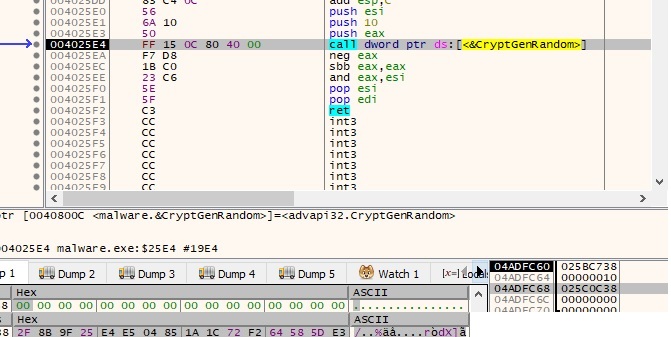
The malicious process uses CryptGenRandom API to generate 32 random bytes which represent an AES256 key and will be used further. Let’s call this key AES1:
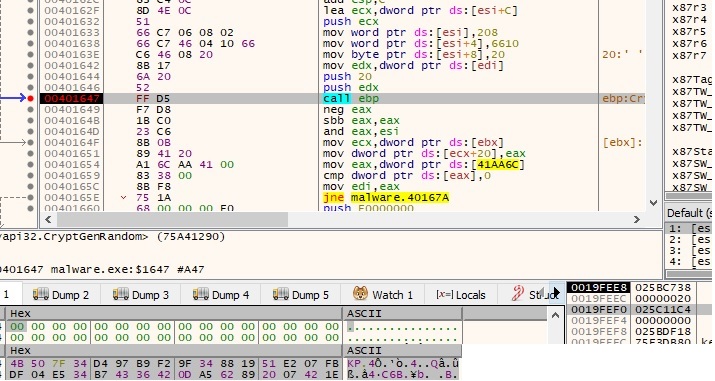
The same process is repeated one more time, we can call the second key AES2:
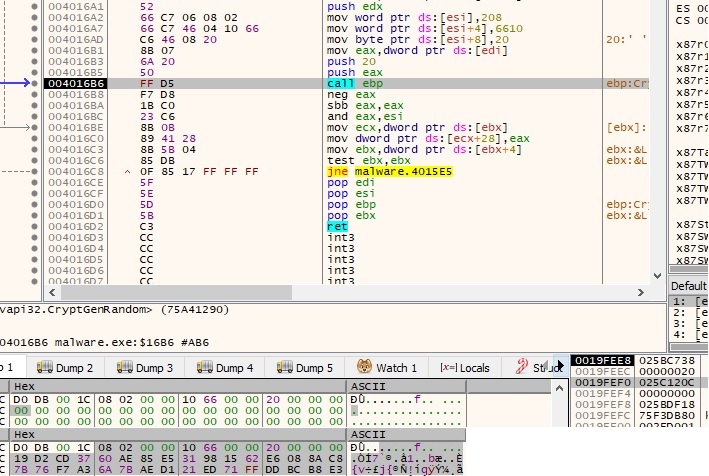
4 bytes (“AD AD A1 A0”) which will be used as a marker are decrypted. The RSA public key which has been decrypted during the first steps is imported using CryptImportKey API:
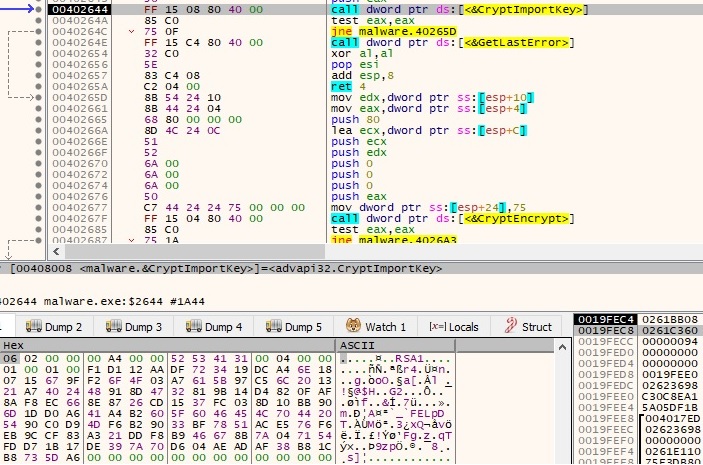
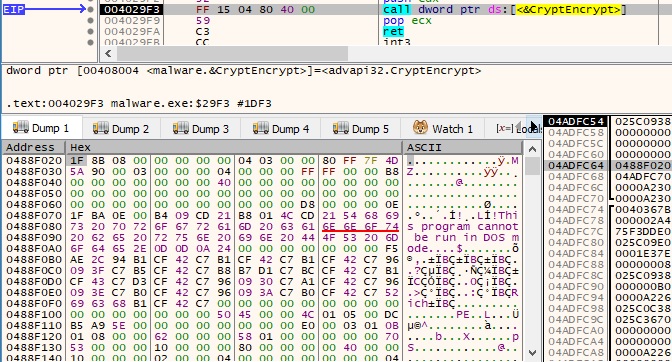
The RSA key encrypts AES1 + other information collected during malware’s execution:
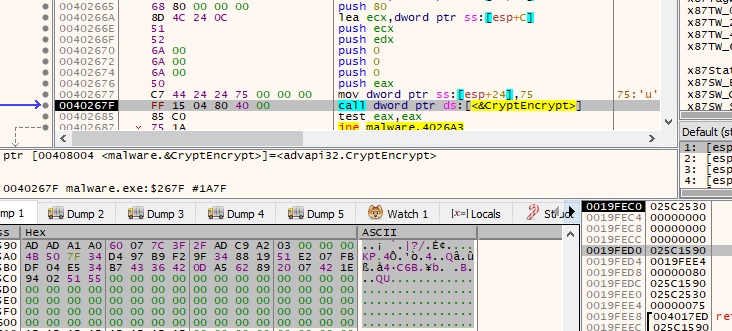
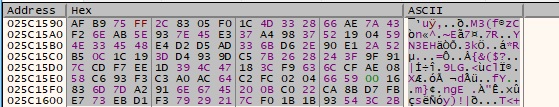
The encryption is applied to AES2 as well:
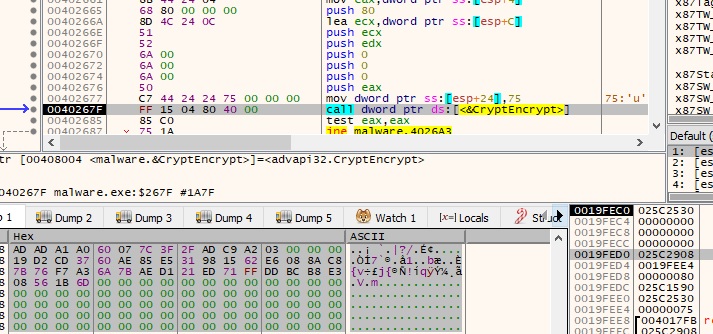
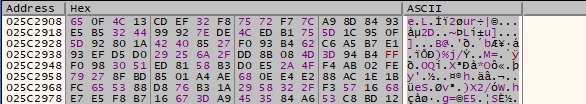
A few more strings are decrypted at runtime, we’ll see their usefulness as we analyze further:
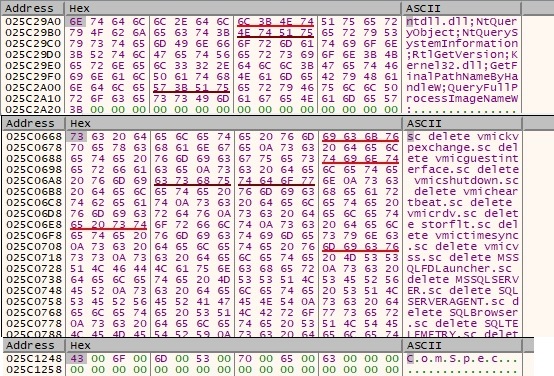
The malicious file creates a new cmd.exe process which is used to delete the list of services decrypted above (the entire list is presented in the appendix) and the shadow copies (common technique used by ransomware):
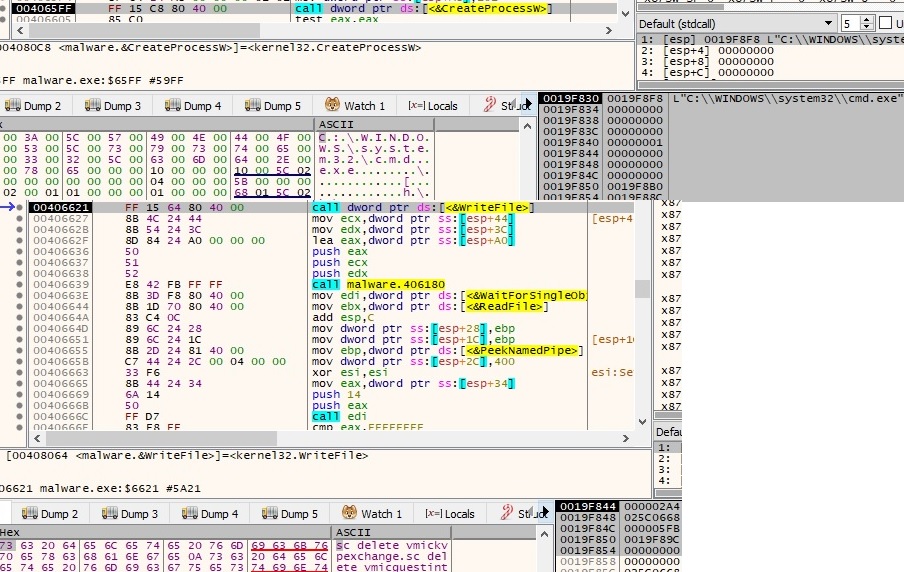
The confirmation of successfully deleting a service is transmitted via a pipe from cmd.exe to our process as shown below:
The malware decrypts a list of processes which will be killed (the full list is written in the appendix). This operation is done using CreateToolhelp32Snapshot, Process32FirstW, Process32Next and TerminateProcess APIs and will ensure that the files which are intended to be encrypted are not locked by these processes:
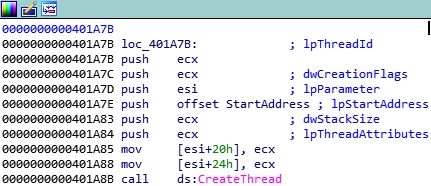
The encryption process starts by creating a thread using CreateThread API. We will see that multiple threads will be created:
The files which are located in the current directory (in our case, Desktop) will be encrypted first. The selection of the files is done using FindFirstFileW and FindNextFileW APIs and they should have an extension which belongs to the list decrypted at runtime (for example .exe and .dll files are not encrypted, the system must remain in a functional state in order to make the payment for decrypting the files). CryptGenRandom function is again used to generate 16 random bytes:
AES1 is being imported and its initialization vector (IV) is set to the newly generated 16 bytes:
Firstly the name of the file is encrypted using AES1:
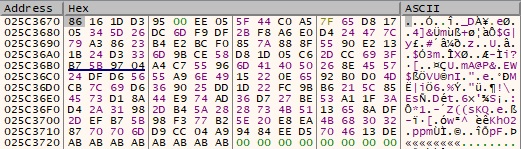
The encrypted file name will be a part of the encrypted file, followed by 4 bytes which represent its length (“B0 00 00 00”, 176 in decimal). The next item which is written is the IV (16 bytes, generated at runtime):
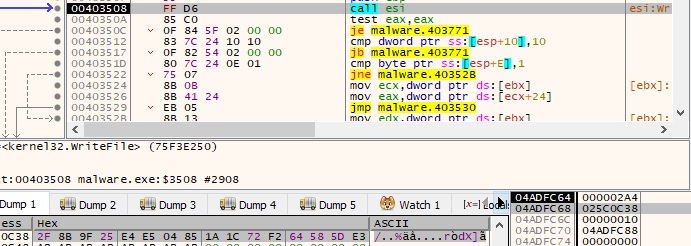
Lastly before encrypting the file content, the malicious process append the encrypted AES1 key:
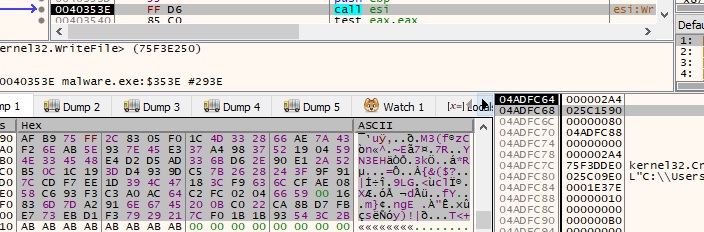
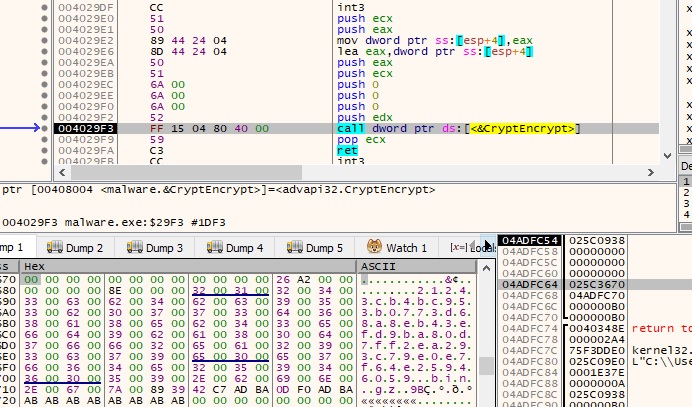
The file content is encrypted using AES1 and the process overwrites the initial file:
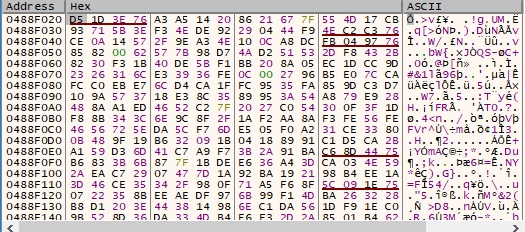
The initial file is renamed and multiple extensions are appended, including the attacker’s email address:
Note: The same steps are also applied to other files but with the second key AES2.
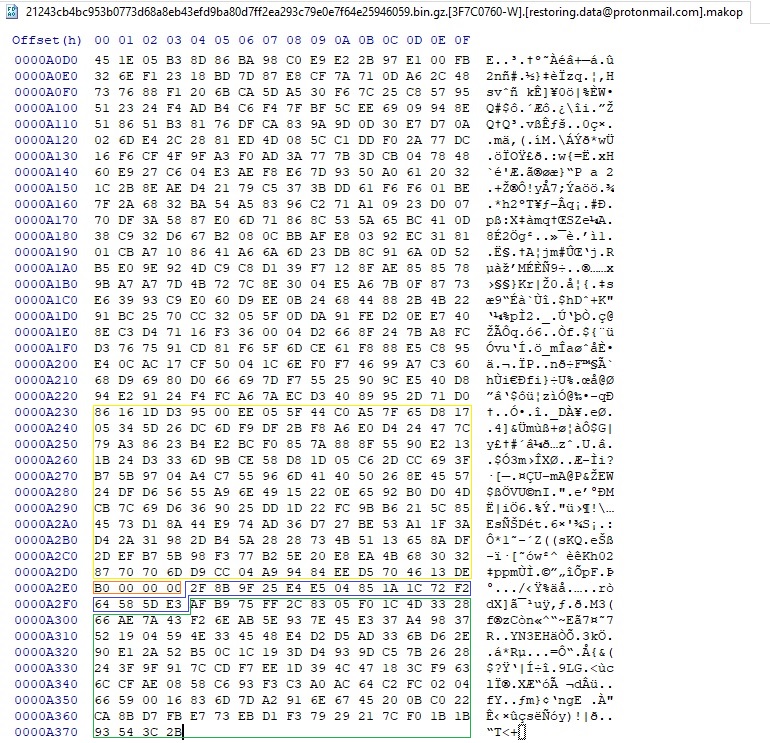
All the encrypted elements are highlighted in the figure below:
The order of targeted directories is the following: Current directory, “C:\”, “C:\ProgramData” and “C:\Users” (one thread for each one). Every file content is encrypted 40000 bytes (40kb) at a time. More information is decrypted at runtime:
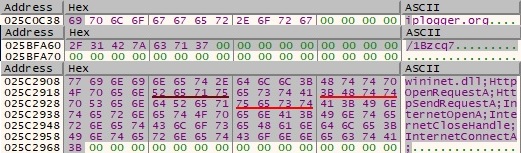
Using InternetOpenA, InternetConnectA, HttpOpenRequestA and HttpSendRequestA APIs the malware is trying to get the victim’s public IP address by accessing hxxps[:]//iplogger.org/1Bzcq7 (we have not seen any other network communication):
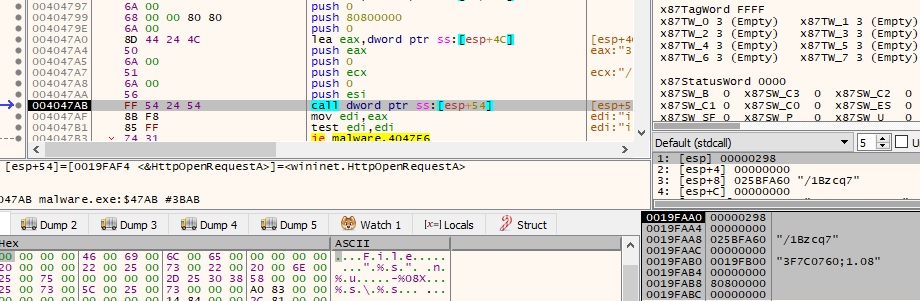
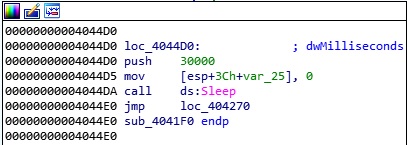
The process sleeps for 30 seconds and then jumps back in order to encrypt the other targeted directories:
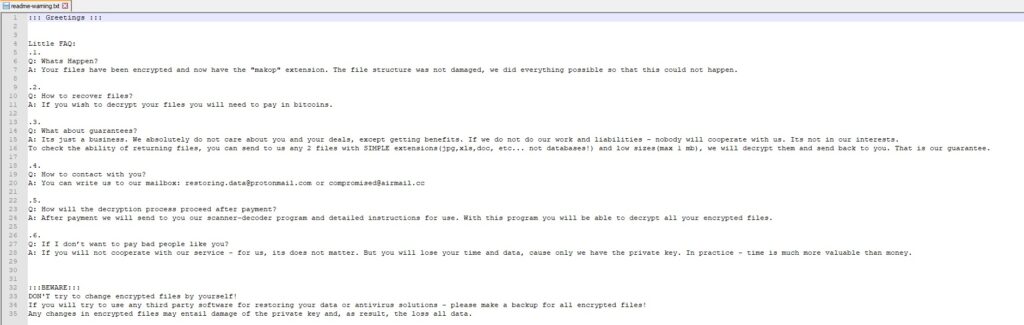
After encryption is complete, it drops a ransom note in every targeted directory:
References
https://www.hex-rays.com/products/ida/support/download_freeware/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/
Appendix
List of services to be deleted + processes which delete shadow copies
sc delete vmickvpexchange
sc delete vmicguestinterface
sc delete vmicshutdown
sc delete vmicheartbeat
sc delete vmicrdv
sc delete storflt
sc delete vmictimesync
sc delete vmicvss
sc delete MSSQLFDLauncher
sc delete MSSQLSERVER
sc delete SQL SERVERAGENT
sc delete SQLBrowser
sc delete SQLTELEMETRY
sc delete MsDtsServer130
sc delete SSISTELEMETRY130
sc delete SQLWriter
sc delete “MSSQL$VEEAMSQL2012”
sc delete “SQLAgent$VEEAMSQL2012”
sc delete MSSQL
sc delete SQLAgent
sc delete MSSQLServerADHelper100
sc delete MSSQLServerOLAPService
sc delete MsDtsServer100
sc delete ReportServer
sc delete “SQLTELEMETRY$HL”
sc delete TMBMServer
sc delete “MSSQL$PROGID”
sc delete “MSSQL $WOLTERSKLUWER”
sc delete “SQLAgent$PROGID”
sc delete “SQLAgent$WOLTERSKLUWER”
sc delete “MSSQLFDLauncher$OPTIMA”
sc delete “MSS QL$OPTIMA”
sc delete “SQLAgent$OPTIMA”
sc delete “ReportServer$OPTIMA”
sc delete “msftesql$SQLEXPRESS”
sc delete “postgresql-x64-9.4”
sc delete WRSVC
sc delete ekrn
sc delete klim6
sc delete “AVP18.0.0”
sc delete KLIF
sc delete klpd
sc delete klflt
sc delete klbackupdisk
sc delete klbackupflt
sc delete klkbdflt
sc delete klmouflt
sc delete klhk
sc delete “KSDE1.0.0”
sc delete kltap
sc delete TmFilter
sc delete TMLWCSService
sc delete tmusa
sc delete TmPreFilter
sc delete TMSmartRelayService
sc delete TMiCRC ScanService
sc delete VSApiNt
sc delete TmCCSF
sc delete tmlisten
sc delete TmProxy
sc delete ntrtscan
sc delete ofcservice
vssadmin delete shadows /all /quiet
wbadmin delete catalog -quiet
wmic shadowcopy delete exit
List of processes to be killed
sqlbrowser.exe
sqlwriter.exe
sqlservr.exe
msmdsrv.exe
MsDtsSrvr.exe
sqlceip.exe
fdlauncher.exe
Ssms.exe
sqlagent.exe
fdhost.exe
fdlauncher.exe
ReportingServicesService.exe
msftesql.exe
pg_ctl.exe
postgres.exe
UniFi.exe
armsvc.exe
IntelCpHDCPSvc.exe
OfficeClickToRun.exe
DellOSDService.exe
DymoPnpService.exe
Agent.exe
FJTWMKSV.exe
IPROSetMonitor.exe
IRMTService.exe
MBCloudEA.exe
QBCFMonitorService.exe
QBIDPService.exe
RstMwService.exe
TeamViewer_Service.exe
dasHost.exe
IntelCpHeciSvc.exe
RAVBg64.exe
vds.exe
unsecapp.exe
TodoBackupService.exe
MediaButtons.exe
IAStorDataMgrSvc.exe
jhi_service.exe
LMS.exe
DDVDataCollector.exe
DDVCollectorSvcApi.exe
TeamViewer.exe
tv_w32.exe
tv_x64.exe
Microsoft.Photos.exe
MicrosoftEdge.exe
ApplicationFrameHost.exe
browser_broker.exe
MicrosoftEdgeSH.exe
MicrosoftEdgeCP.exe
RtkNGUI64.exe
RAVBg64.exe
WavesSvc64.exe
OneDrive.exe
DYMO.DLS.Printing.Host.exe
FtLnSOP.exe
FjtwMkup.exe
FTPWREVT.exe
FTErGuid.exe
qbupdate.exe
QBWebConnector.exe
ShellExperienceHost.exe
RuntimeBroker.exe
IAStorIcon.exe
PrivacyIconClient.exe
SupportAssistAgent.exe
SecurityHealthService.exe
taskhostw.exe
taskhosta.exe
wijca.exe
ktfwswe.exe
HeciServer.exe
mdm.exe
ULCDRSvr.exe
WLIDSVC.EXE
WLIDSVCM.EXE
GoogleCrashHandler.exe
GoogleCrashHandler64.exe
RAVCpl64.exe
igfxtray.exe
hkcmd.exe
igfxpers.exe
PsiService_2.exe
UNS.exe
taskeng.exe
AdobeARM.exe
rdpclip.exe
LenovoReg.exe
LMS.exe
dwm.exe
taskeng.exe
wuauclt.exe
armsvc.exe
avp.exe
OfficeClickToRun.exe
FBService.exe
Jhi_service.exe
LBAEvent.exe
PDFProFiltSrvPP.exe
avpsus.exe
IAStorDataMgrSvc.exe
klnagent.exe
vapm.exe
UNS.exe
unsecapp.exe
RAVCpl64.exe
ScanToPCActivationApp.exe
BrStMonW.exe
BrCtrlCntr.exe
concentr.exe
redirector.exe
BrccMCtl.exe
BrYNSvc.exe
Receiver.exe
BrCcUxSys.exe
LSCNotify.exe
SelfServicePlugin.exe
wfcrun32.exe
HPNETW~1.EXE
HPScan.exe
taskhost.exe
Teams.exe
AuthManSvr.exe
WLXPhotoGallery.exe
outlook.exe
prevhost.exe
excel.exe
chrome.exe
AcroRd32.exe
RdrCEF.exe
vssadmin.exe
WmiPrvSE.exe
oracle.exe
ocssd.exe
dbsnmp.exe
synctime.exe
agntsvc.exe
mydesktopqos.exe
isqlplussvc.exe
xfssvccon.exe
mydesktopservice.exe
ocautoupds.exe
encsvc.exe
firefoxconfig.exe
tbirdconfig.exe
ocomm.exe
mysqld.exe
mysqld-nt.exe
mysqld-opt.exe
dbeng50.exe
sqbcoreservice.exe
infopath.exe
msaccess.exe
mspub.exe
onenote.exe
powerpnt.exe
steam.exe
thebat.exe
thebat64.exe
thunderbird.exe
visio.exe
winword.exe
wordpad.exe
Good start! Thank you, Vlad!
Este super tare! Foarte fain!